-객체지향 복습
상태/행동 => 객체
**객체생성하는 방법
-
객체 구상 : 여러 객체를 구현해서 표현해야겠다.
-
클래스를 만듭니다. -> 멤버변수(상태), 멤버메소드(기능)
-
객체 생성 전 생성자를 만듭니다.(필요한 수대로 파라미터를 만들어 초기화한다.) ,필요한만큼 니즈대로 생성자 생성
-
객체를 생성합니다.
-
의존(점선) : 특정 메소드 안에서 사용함& 연관관계(실선) 파악
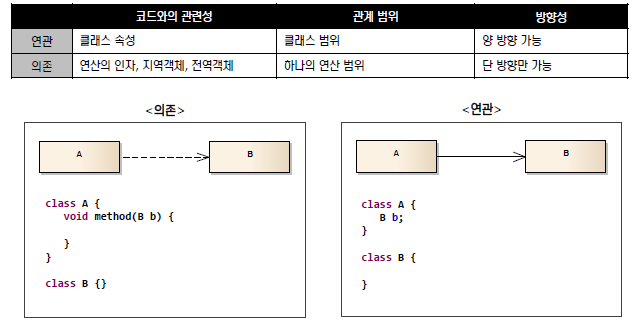
Bank Mission

-Main함수가 작동하게끔 나머지 MyBank, Customer, Account클래스 작성하기
package Kosta.bank;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class BankSystem {
private MyBank myBank; //MyBank
public BankSystem(){ //생성자
myBank = new MyBank();
showMenu();
}
public void showMenu(){ //show method 만들기
String menu = null;
String id = null;
String name = null;
long balance = 0;
do{
System.out.println("****메뉴를 입력하세요****");
System.out.println("1. 고객등록");
System.out.println("2. 고객보기(1명)");
System.out.println("3. 고객전체보기");
System.out.println("4. 고객예금출금");
System.out.println("5. 고객예금입금");
System.out.println("***끝내기***");
System.out.println("***************");
System.out.print(">>");
menu = readFromKeyboard();
if(menu.equals("1")){ //고객등록
System.out.print("ID를 입력하세요: ");
id = readFromKeyboard();
System.out.print("이름을 입력하세요: ");
name = readFromKeyboard();
System.out.print("잔고를 입력하세요: ");
balance = Long.parseLong(readFromKeyboard());
myBank.addCustomer(id, name, balance);
}
else if(menu.equals("2")){
System.out.print("고객ID를 입력하세요: ");
id = readFromKeyboard();
Customer cust = myBank.getCustomer(id);
System.out.println(cust.getID() +":" + cust.getName() + ": "
+ cust.getAccount().getBalance());
}else if(menu.equals("3")){
Customer[] allCust = myBank.getAllCustomer();
//배열복사를 이용해 예외가 안일어나게 해야함. ->null point exception이 발생
for(int i=0;i<allCust.length;i++){
System.out.println(allCust[i].getID() + ": " + allCust[i].getName() + " :" +
allCust[i].getAccount().getBalance());
}
}else if(menu.equals("4")){
System.out.print("고객의 ID를 입력하세요.: ");
id = readFromKeyboard();
Customer cust = myBank.getCustomer(id);
if(cust == null){
System.out.println("등록된 고객이 아닙니다.");
}else{
System.out.print("출금액을 입력하세요: ");
balance = Long.parseLong(readFromKeyboard());
if(cust.getAccount().withdraw(balance)){
System.out.println("정상적으로 출금되었습니다.");
System.out.println("출금후 잔고는 :" + cust.getAccount().getBalance());
}else{
System.out.println("잔고가 부족합니다.");
}
}
}else if(menu.equals("5")){
System.out.print("고객의 ID를 입력하세요.: ");
id = readFromKeyboard();
Customer cust = myBank.getCustomer(id);
if(cust == null){
System.out.println("등록된 고객이 아닙니다.");
}else{
System.out.print("입금액을 입력하세요: ");
balance = Long.parseLong(readFromKeyboard());
cust.getAccount().deposit(balance);
System.out.println("정상적으로 입금되었습니다.");
System.out.println("입금후 잔고는 :"+ cust.getAccount().getBalance());
}
}
}while(!menu.equals("q"));
}
public String readFromKeyboard(){
String input = null;
try{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
input = br.readLine();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return input;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankSystem bank = new BankSystem();
}
}
package Kosta.bank;
public class MyBank {
private Customer[] customers;//배열 선언상태
private int customersNum;
public MyBank(Customer[] customers, int customersNum) {
super();
this.customers = customers;
this.customersNum = customersNum;
}
public MyBank(){
customers = new Customer[10];//배열 생성
}
public void addCustomer(String ID, String name, long balance) {
//Customer 객체 생성후 배열에 추가
customers[customersNum++] = new Customer(ID,name,balance);
}
public int getCustomerNum() {
return customersNum;
}
public Customer getCustomer(String ID) {
//id에 해당하는 customer객체 구하기
//지역변수 cust
Customer cust = null;
for(int i=0;i<customersNum;i++) {
if(customers[i].getID().equals(ID)) {
cust = customers[i];
break;
}
}
return cust;
}
public Customer[] getAllCustomer() {
Customer newCustomers[] = new Customer[customersNum];
System.arraycopy(customers, 0, newCustomers, 0, customersNum);
return newCustomers;
}
}
package Kosta.bank;
public class Customer {
private String ID;
private String name;
private Account account;
public Customer(String ID, String name, long balance) {
super();
this.ID = ID;
this.name = name;
this.account = new Account(ID,balance);
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setID() {
this.ID = ID;
}
public String getID() {
return ID;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
package Kosta.bank;
public class Account {
private String ID;
private long balance;
public Account(String ID, long balance) {
super();
this.ID = ID;
this.balance = balance;
}
public void deposit(long amt) {
balance += amt;
}
public boolean withdraw(long amount) {
if(balance <amount) {
return false;
}
balance -=amount;
return true;
}
public String getID() {
return ID;
}
public long getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
***Galaga문제
package Kosta.galaga;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainLec {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); //대신 string써도됨
for(int i=0;i<t;i++) {
sb.append("#" + (i+1) +" "+deep(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt(), 0));
sb.append("\n");//append대신 +써도 됨.
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
public static int deep(int a, int b, int day) {//다른 클래스 안쓰니 static선언
if(b>a) {
return day;
}else {
return deep(a*2,b*3,day+1);
}
}
}
**상속
자바 -> 확장성 : 보다 효율적으로 확장하기 위해 상속을 사용합니다.
상속 - 기존 클래스와 유사한 클래스를 만들어야 할 경우(확장해서 새로운 클래스를 만듦 -> 새로운 제품탄생!)
자바에서는 부모를 선택할 수 있음.
이런 상속을 통해 스레드, 예외클래스,서블릿을 구현할 수 있음.

package Kosta.oop2;
public class CheckingAccount extends Account {
private String cardNo;
public int pay(String cardNo, int amount) throws Exception{
if(!cardNo.equals(this.cardNo)|| balance < amount) {
throw new Exception("결제 불가");
}
return withdraw(amount);
}
}
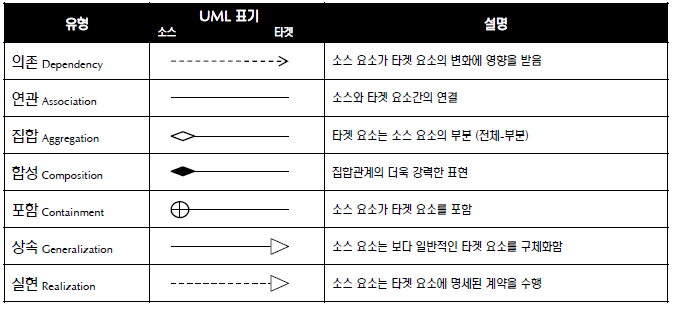
집합과 합성관계는 둘다 연관관계에서 파생된 것임.
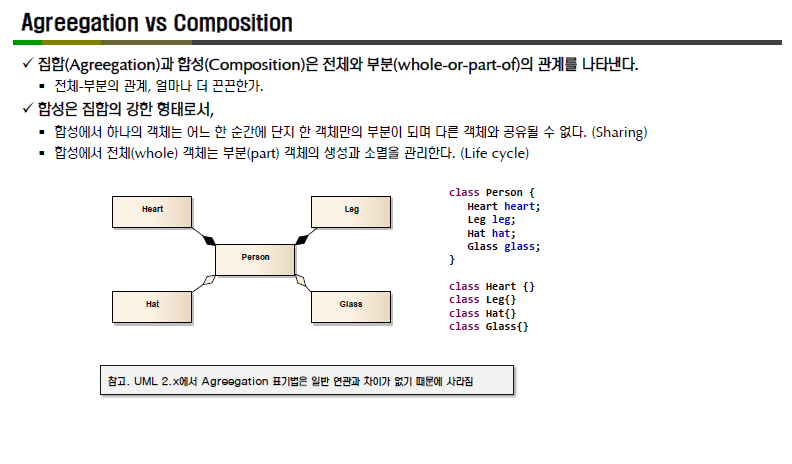
-집합관계 : 떼어낼 수 있는 것. 다른 클래스에서도 사용되어질 수 있는 것.
-합성관계 : 하나의 객체는 어느 한 순간에 단지 한 객체의 부분이 되며 다른 객체와 공유될 수 없다.

a = new CheckingAccount;
a.deposit (메모리에 있으니까 사용가능하다)
자식을 생성하면 부모도 생성될 수 밖에 없다.
나의 생성자 호출 전에 부모의 생성자를 먼저 호출하러 간다. (부모 영역의 메모리가 생성되었다.)
내가 지정하지 않으면 부모의 default생성자를 호출하러 간다. (파라미터 값이 아무것도 없는 것)
부모의 default생성자를 안만들어놓으면 나중에 상속할 때 에러 뜸.
-Account를 상속받은 CheckingAccount
package Kosta.oop2;
public class Account {
String ownerName;
String accountNo;
double balance;
public Account() {};
public Account(String ownerName, String accountNo, double balance) {
super();
this.ownerName = ownerName;
this.accountNo = accountNo;
this.balance = balance;
}
public void deposit(int amount) {
balance += amount;
}
public int withdraw(int amount) throws Exception {
if(balance<amount) {
throw new Exception("잔액 부족");
}
balance -= amount;
return amount;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("계좌번호: "+ accountNo);
System.out.println("계좌주: "+ ownerName);
System.out.println("계좌잔액: "+ balance);
}
public int update(int i) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
}
package Kosta.oop2;
public class CheckingAccount extends Account {
private String cardNo;
public CheckingAccount(String ownerName, String accountNo, double balance, String cardNo) {//부모생성자 초기화
super(ownerName, accountNo, balance); //부모생성자
this.cardNo = cardNo;
}
public CheckingAccount() {}
public int pay(String cardNo, int amount) throws Exception{
if(!cardNo.equals(this.cardNo)|| balance < amount) {
throw new Exception("결제 불가");
}
return withdraw(amount);
}
}
package Kosta.oop2;
public class CheckingMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CheckingAccount ca =
new CheckingAccount("111-111","홍길동",10000,"111-111");
try {
ca.pay("111-111",4000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ca.print();
}
}
**video (GeneralMember를 상속받은 SpecialMember작성하기)
package Kosta.video;
public class SpecialMember extends GeneralMember {
private int bonus;
public SpecialMember (){}
public SpecialMember(String ID, String name, String address, int bouns) {
super(ID, name, address);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public void print() {
super.printmember();
System.out.println("회원의 보너스 포인트 : "+ bonus);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Video v1 = new Video("1","트랜스포머3","서봉수");
Video v2 = new Video("2","쿵더팬더2","지성민");
// GeneralMember m1 = new GeneralMember("aaa","홍길동","동탄");
// GeneralMember m2 = new GeneralMember("bbb","김철수","서울");
SpecialMember s1 = new SpecialMember("bbb", "김철수", "서울", 10);
s1.setBorrowvideo(v2);
// m1.setBorrowvideo(v1);
// m2.setBorrowvideo(v2);
s1.printmember();
s1.print();
}
}
----정리
-
상속은 왜하는가? ->확장성이 좋아지기 때문에
-
상속하는 방법 : extends 키워드하나면 끝난다.
-
상속시 자식을 생성하면 부모가 생성되고, 부모의 생성자를 먼저 호출하고 자식의 생성자가 제일 마지막에 호출된다.
-
부모생성자는 기본적으로 default생성자가 호출되지만 내가 임의로 인자가 많을 때 super함수를 이용하여 파라미터가 있는 생성자를 지정해줄 수 있다.
-
상속이유 : 자식입장에서 부모의 변수나 메소드를 내맘대로 사용할 수 있다.
-
super(), super 사용하는 용도
***에러뜨면
-내가 부모의 클래스에 default생성자를 만들어주든가
-super를 이용하여 다른 인자가 있는 부모생성자를 선택하든가
내일배울것 : 오버라이딩 -> 형변환 -> 자바의 다형성
final string -> 상속이 안됨.
**StringBuffer란 무엇인가
super() : 자식의 생성자에서 조상의 생성자를 호출할 때.
this : 멤버변수와 지역변수의 이름을 구분할 때 사용
super : 상속받은 멤버와 자신의 멤버의 이름이 같을 때 구분하기 위해 사용, 자식의 메소드에서 부모의 메소드를 호출할 때
엉뚱한 클래스를 상속하지 않도록 주의
연관관계 vs. 상속관계
-Rectangle을 상속받은 Square 작성해보기 미션
**선택 정렬은 앞으로 작은 수를 보내는 것 : <JAVA 5차시>, <JAVA 6차시>
**버블 정렬은 뒤로 큰 수를 보내는 것
우선순위는 1.2.3.4.5복습
MISSON-버블 정렬해보기 + 재귀함수로 해보기

